What is multi factor authentication (MFA)?
Many organizations today rely on multi-factor authentication (MFA) to prevent identity theft.
How does multi factor authentication work? Multi factor authentication, also known as MFA, is a type of security measure that requires more than one method of verification from users before granting them access to a system. Typical types of multi factor authentication (MFA) are:
- Something that the user knows (like a password or the answer to a security question)
- Something that the user has (like their phone or another device)
- Other unique identifiers (like their fingerprint or face)
In addition, recent technical breakthroughs have enabled novel multi factor authentication solutions. One example is ‘behavioral biometrics’, which can recognize and authenticate people based on things like their typing style, physical gestures, and mouse usage.
Why is multi factor authentication important?
Sadly, identity theft is more common than ever. There are various reasons for this, from weak and easy to guess passwords to the fact that hackers have become increasingly good at stealing them. Because of this, multi factor authentication, or MFA, is an important security measure that can help protect your identity. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide more than just their password before they are authenticated.
Multi factor authentication (MFA) examples:
- Google's 2-step verification process
- Microsoft authenticator
- Push notifications on your phone (e.g., Duo Security or Okta)
- Face and fingerprint recognition on smartphones
Two factor authentication (2FA) vs. Multi factor authentication (MFA)
What is MFA vs. 2FA? Two factor authentication (2FA) is exactly two factors of authentication, such as password and phone app approval. Multi factor authentication (MFA) is a generalization of that concept and could include other factors. Normally the terms are used interchangeably. It basically means you need an extra step other than your password to prove your identity.
The benefits of multi factor authentication (MFA)
Multi factor authentication (MFA) is highly effective. In fact, MFA can stop up to 99.9% of cloud identity thefts. This is because the attacker must provide multiple forms of verification in order to gain access, which they are very rarely able to do. Even if an attacker steals or guesses a password, it is highly unlikely that they will also have access to another form authentication such as a smartphone (to approve a push notification) or biometrics (fingerprints, facial ID).
Here are some more benefits of multi factor authentication:
- It’s budget friendly: Unlike solutions that rely on AI and require an army of data scientists, MFA can fit into large and small budgets.
- It’s easy to deploy: MFA has been around for some time and requires little training.
- It helps security teams by eliminating much of the tactical work of chasing false positives (not to mention the excess number of alerts they get).
Challenges of multi factor authentication
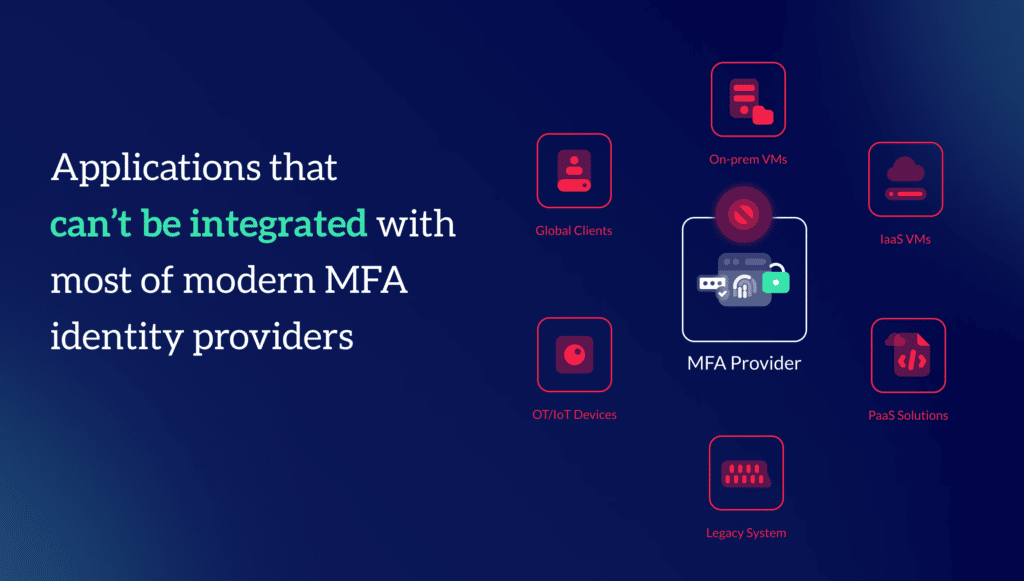
So, if multi factor authentication (MFA) prevents 99.9% of cloud identity theft, why are attackers still winning and in ever growing numbers? While MFA can help protect cloud identities for SaaS applications, organizations have a lot more than just these SaaS applications. For example: IaaS virtual machines, PaaS solutions, on-prem servers and VMs, clients spread across the globe, various legacy applications, and OT/IOT devices that can’t integrate with most modern MFA identity providers.
The Zero Networks Solution
Zero Networks can extend MFA provider of choice, putting it in front of any application or administrative tool your IT and DevOps teams are using. And this is done before the network port for that application or admin tool is even open. All the important ports and admin tools attackers love to use are closed, so that the attacker can’t even see them. This approach leaves zero attack surface (pun intended) and stops attackers from spreading in the organization.
About Zero Networks
Zero Networks is solving the biggest challenge in cybersecurity: making military-grade network security available to everyone, regardless of skill, size or complexity. For years, microsegmentation has been the promised land, but could never be achieved at scale. MFA, which should be the ultimate security measure, can’t fit every service and every protocol. As a result, networks remain open from the inside, and attacker’s jobs are easy once they get into at least one machine inside the network.
Zero Networks, instead, creates a new paradigm. One that makes microsegmentation fast, easy, effective, and deployable by anyone. This modern approach is self-service and automated, eliminating the need for agents while leveraging your host-based firewall for enforcement.
Zero Networks is proud to work with companies large and small around the world, helping them protect their networks from breaches and ransomware.
Reduce the risk of breaches to almost zero with Zero Networks' MFA-based micro segmentation solution.



