Ransomware vs. Ransomware Attack?
Before diving deeper into the technicalities, it is important to make a distinction. The term “ransomware” is often conflated with “ransomware attack”. However, there is a big difference between the two.
While ransomware is a piece of malicious code that usually encrypts data, a ransomware attack is a complex operation that closely resembles how a company operates. It consists of many people, such as coders, operators, managers, researchers, bookkeeping, and more. The ransomware sample itself is usually the final stage of a ransomware attack, deployed only after the attackers discover a viable distribution vector.
The length of a ransomware attack can be anywhere between several hours to several weeks or even months, during which time the attackers get a foothold inside the organization and perform lateral movement in order to compromise as many assets as they can and escalate their privileges. Once the attackers manage to compromise a “strong” account (usually a domain administrator), they utilize this account to spread the actual ransomware sample across the network, sometimes this can also be achieved without admin credentials by simply using some known vulnerabilities that aren’t patched yet. This is when skulls start to appear on computer screens with ticking timers, and the victims understand (albeit too late) that they have been compromised.
Ransomware Recovery and Ransomware Removal
From the moment that the ransomware has been distributed, ransomware removal and recovery is needed, as all the data is now encrypted. This is normally the same operation, as one of the best methods to recover a host is to reinstall a “clean” OS. However, data is not the only thing that needs to be “recovered” – as all of the credentials, secrets, API keys and private keys could also have already been compromised, they should also be regenerated to ensure that the ransomware attack won’t hit again.
Why Ransomware Attacks Became so Prevalent
According to the most recent Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR), ransomware accounts for 70% of malware-related breaches, and for 25% of all data breaches – it is the fastest-growing hacking “trend”.
The number 1 driver for any attacker group is (unsurprisingly) profit. In the not-so-distant past, making a profit out of a security breach was not a trivial task. Hackers had to maintain a complex ecosystem that somehow turned all their stolen data into money. For example, they could sell stolen data over the dark web. This process was not trivial and made turning a profit out of hacking quite a cumbersome task. However, this was about to change with the introduction of cryptocurrency.
When cryptocurrency started to gain traction, attackers were quick to realize its potential. It meant they could receive payments from victims while staying anonymous and beyond the reach of governments. At the same time, they didn’t have to worry about how to monetize compromised data. As it turns out, the owner of the data usually is the one willing to pay the most for it. The first modern ransomware attack was CryptoLocker, which grossed more than $27M in bitcoin.
Why Ransomware Attacks are Hard to Stop?
The adversaries behind many ransomware attacks are very sophisticated. Because the ransomware business is so profitable, they can hire top talent that enables them to find zero-days, create their own customized tools (which are harder to detect), and research advanced evasion techniques that help them remain undetected by (so-called) advanced security solutions. Examples of such techniques are Hypervisor Jackpotting and bypassing EDRs. Ransomware gangs have the resources and skills that were once believed to only exist for nation states, meaning their victims need nation-grade defenses in order to tackle such attacks.
How To Prevent Ransomware Attacks
As we already established – ransomware attacks are not “one thing” - they are sophisticated and complex. This means you need to set up a strong protection against any form of attack against your network, assuming your network has already been breached.
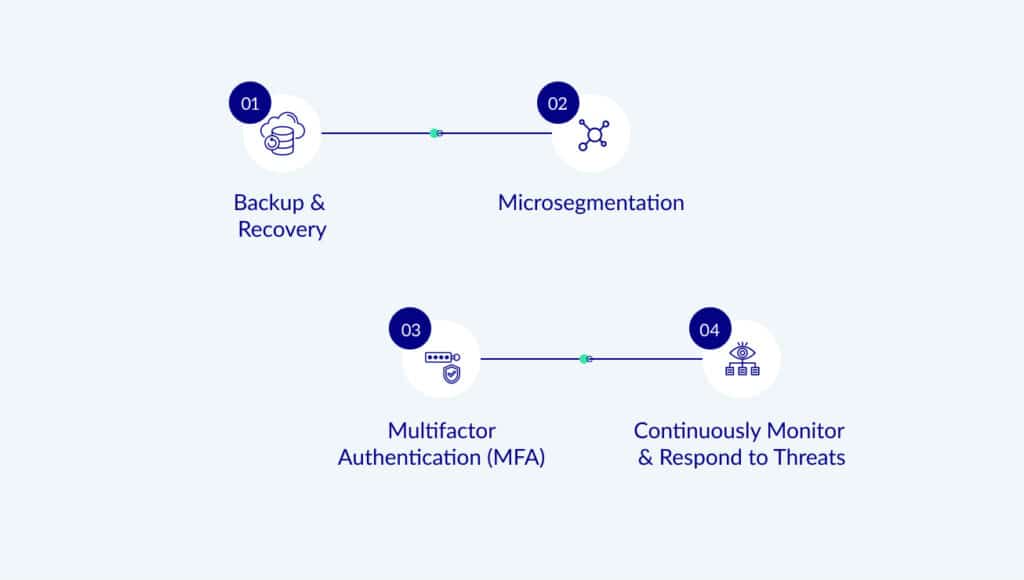
- Backup & Recovery: in the unfortunate scenario that your data has been encrypted, make sure you have the option to recover from a backup. It is crucial that this backup system is separate from the main network and can only be accessed securely (otherwise it is also in jeopardy). Having the data backed up is not enough though. An efficient recovery of the OS and resetting of all credentials is also required, in order to ensure that the same attack group won’t simply reuse their access to hit the same target again.
- Microsegmentation: 100% of ransomware attacks need network access to propagate. From the very early stages of an attack, when they scan the internal network, to the latter ones, where they exploit a vulnerable exposed service or utilize compromised credentials to propagate. A segmented network leaves attackers stranded, so there is almost nothing they can do to spread.
- MFA: Credentials are probably the most utilized “weapon” by attackers, who often find it too easy to steal or crack. While MFA is not immune to attacks, it will definitely create a big challenge for attackers when they try and compromise credentials. By upgrading access (especially privileged access) to be protected with MFA, you are far less likely to suffer an attack.
- Continuously Monitor and Respond to Threats: Attackers are human, they make mistakes and trigger alerts across your organizations. Do not ignore suspicious activity in your network, and make sure you respond in time to meet a potentially emerging threat.
The Zero Networks Solution
Zero Networks is a military-grade, MFA-based microsegmentation solution. It prevents ransomware attacks from scanning the network (as there is far less to scan), finding and exploiting vulnerabilities, and propagating to other assets in the network. Even if credentials are compromised, the Zero Networks just-in-time MFA approach ensures that these credentials cannot be utilized.
About Zero Networks
Zero Networks' goal is to solve the hardest security challenges out there, by making military-grade network security available to everyone, from small offices to large enterprises. For years, microsegmentation solutions remained out of reach to most organizations due to their cost, difficulty to deploy, as they required agents, and being almost impossible to scale, as configuration is manual. This resulted in networks remaining open even after microsegmentation solutions were deployed.
The new paradigm by Zero Networks makes microsegmentation easy, simple and effective. It can be deployed by anyone, as this modern approach is self-service and automated.
Zero Networks helps customers across industries and from any region defend themselves against the most sophisticated attacks, data breaches and ransomware.



