TL;DR
Zero Trust Security is a model that eliminates implicit trust in networks by continuously verifying user identities, device health, and access patterns. It restricts access to only authorized users and devices through granular, context-aware policies to prevent lateral movement across networks.
What is Zero Trust Security?
This question has been echoing in the corridors of cybersecurity and IT departments across industries. Zero Trust Security, a revolutionary approach to data security, redefines the traditional trust architecture by eliminating implicit trust from networks.
Let’s uncover the fundamentals of Zero Trust Security and its journey to how it is defined today, as well as examine why organizations need it and how companies like Google have adopted it. From understanding its basics to exploring its origin and evolution, we aim to equip you with comprehensive knowledge about this game-changing concept.
Below, we delve deeper into why your organization needs a true zero-trust model and how leading companies like Google have successfully implemented it. Further sections dissect the key tenets guiding implementation while also discussing challenges in achieving effective zero trust methods like microsegmentation.
Lastly, we provide additional resources for further reading on this topic - including relevant articles, research papers, and case studies – solidifying your understanding of what is zero trust security.
Understanding Zero Trust Security
In the world of cybersecurity, Zero Trust challenges the old belief that everything inside a network can be trusted. It's asserting, "Hey, let's not assume anything and verify everything."
The Basics of Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust doesn't care if you're inside or outside the network perimeter. It treats every access request as suspicious and demands proof of identity before granting entry.
How does Zero Trust work?
Zero Trust is like a detective that continuously investigates each user and device trying to access the network. It probes the identity, condition, and position of each user/device wanting to enter the network, in order to detect malicious activities.
This approach creates mini fortresses around each resource, making it harder for attackers to move around undetected.
Origin and Evolution of Zero Trust
The concept of Zero Trust Security isn't new. The Black Core Network Initiative, a military-style approach to cybersecurity, was created with the intention of completely blocking any external or internal unapproved access to the core network.
Birthplace of the Zero Trust concept
The term 'Zero Trust' was coined by John Kindervag, a former analyst at Forrester Research, in 2010. The idea behind this model is simple yet powerful - don't trust anyone or anything; always verify. This marked a departure from traditional perimeter-based security models where once you're inside the network, you're trusted.
Evolution over time
Over time, as technology evolved and threats became more sophisticated, so did the Zero Trust model. Today's interpretation extends beyond just networks to data, people, devices, and workloads for comprehensive protection against cyber threats.
- In 2014, Google launched an initiative called BeyondCorp, shifting away from VPNs towards ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access) based on user identity and device state.
- In recent years, there has been increased interest due to rising cloud adoption and remote working trends, making traditional perimeters obsolete.
- Cybersecurity vendors have started offering solutions built around these principles, providing capabilities like microsegmentation, least privilege access, etc., further driving adoption across industries.
This evolution shows how organizations are increasingly recognizing that they can't rely solely on perimeter defenses anymore but need to adopt a more holistic approach encompassing all aspects of their IT environment. As we move forward into an era dominated by digital transformation initiatives such as IoT, AI, and ML, having robust cybersecurity measures like Zero Trust will be paramount.
Key Takeaway:
The concept of Zero Trust security, which originated from the military's Black Core Network Initiative, emphasizes the need to constantly verify and not trust anyone or anything. Over time, it has evolved to encompass all aspects of an organization's IT environment, with increased interest due to cloud adoption and remote working trends. This evolution highlights the recognition that relying solely on perimeter defenses is insufficient in today's digital transformation era dominated by IoT, AI, and ML initiatives.
Why Does Your Organization Need Zero Trust?
Breaches are increasingly common, and more damaging than ever. Zero Trust networking is a game changer that gives security teams the upper hand. If attackers cannot even see targets because all the communication ports are closed, they are completely stuck.
The Zero Trust framework is the gold standard for network security and is used by the world’s leading technology companies. For example, Google, where all connections in its internal network are closed until it’s necessary for them to be open. Users must go through MFA (Multi Factor Authentication) before getting network access to any internal application or server. At any given time, there are very few connections open, which virtually eliminates the attack surface.
In fact, this is exactly what Zero Networks automates, essentially providing a Google-worthy network security stack, and zero-trust architecture, in a matter of minutes as a service for our customers.
Principles for a Truly "Zero Trust" Model
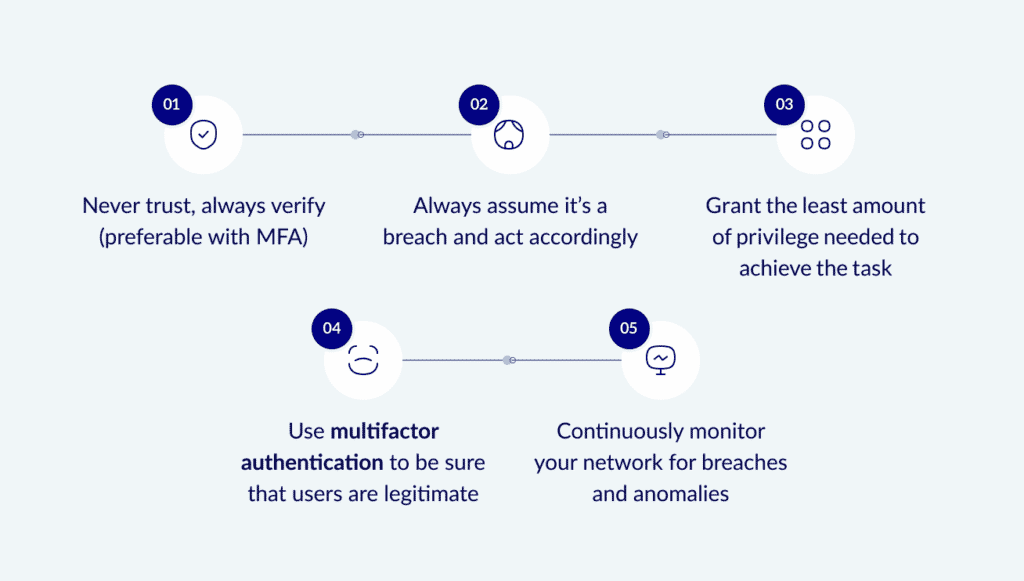
The concept of Zero Trust Security isn't a one-size-fits-all solution. It's guided by five key principles that are crucial to understanding what makes a system truly "zero trust." Let's uncover these essential tenets.
The Five Key Tenets
- Verify Explicitly: Always authenticate and authorize based on all available data points, including user identity, location, device health, and the service or workload the user is interacting with.
- Assume Breach: Regardless of where it's located or how secure you think it is. This principle ensures continuous verification and validation of each request.
- Use Least Privilege Access: Limit user access with just-in-time and just-enough-access (JIT/JEA), risk-based adaptive policies, and data protection to prevent lateral movement within your network.
- Deploy Multifactor Authentication: Use MFA to be sure that all users are legitimate.
- Continuously Monitor: Continuously monitor your network for breaches and anomalies, Leverage analytics and automation processes for improved threat detection response times.
In essence, implementing true zero trust requires an organization-wide transformation in mindset from traditional perimeter-based defenses towards comprehensive visibility across users' identities and their interactions with corporate resources. It calls for constant vigilance - every action must be verified; nothing should be trusted blindly.
Beyond these guiding principles lies another critical factor: choosing the right cybersecurity partner who understands your unique business needs while ensuring seamless integration without disrupting existing workflows.
Key Takeaway:
The principles of a truly "Zero Trust" model in cybersecurity are outlined, including verifying explicitly, using least privilege access, assuming breach, implementing microsegmentation, and leveraging analytics and automation. It is emphasized that true zero trust requires a shift in mindset towards comprehensive visibility and constant vigilance.
Challenges with Zero Trust
A big challenge can be finding a vendor who provides true Zero Trust networking. A lot of security vendors will claim to give you some form of zero trust network access, but many of them are just using the words “Zero” and “Trust” in their marketing materials. Out of the hundreds of vendors out there that claim to provide real Zero Trust, very few actually do.
Of those that do provide Zero Trust Networking, there are two main models: ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access) which provides you with Zero Trust from the outside, and Microsegmentation which provides you with Zero Trust from the inside, e.g., between machines within your network. To achieve real Zero Trust segmentation, organizations must combine these two solutions.
You can read about the challenges related to microsegmentation here. ZTNA, since it's similar to reverse proxy technology that sits in the vendor's cloud, comes with its own set of challenges:
- Going through the vendor’s cloud usually means more latency and less bandwidth = bad user experience.
- Cloud networking is expensive. Guess who is going to pay for that? (hint: not the vendor)
- Having reverse proxy obfuscates all the user traffic through a single entity. Various detection solutions break down in that scenario.
The amount of work needed to combine these two models, and have them well-coordinated and working together, is also an enormous challenge.
Zero Networks' Solution
Zero Networks offers an innovative combination of microsegmentation and ZTNA (with the addition of automation and self-service). Zero Networks solves all the pain points of each of these solutions with a single holistic solution.
To sum up how Zero Networks achieves this:
- We automatically microsegment every asset in the organization. That way no ports are left open unless they’re needed. And even when they are needed, they are only opened if it’s not risky.
- We apply MFA-based restrictions against the privileged protocols that attackers love to use (risky).
- We make sure that normal, non-admin usage is uninterrupted.
In summary, Zero Networks offers an agentless, automated approach to Zero Trust for network security. We combine microsegmentation and Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) into a simple, unified platform for secure remote connectivity and software-defined segmentation for any asset: IT/OT, on-prem, or in the cloud.
About Zero Networks
Microsegmentation means that every module in the environment should only be able to access the information and resources necessary for legitimate purposes. Great idea – in theory – that few organizations practice. Sadly, past efforts at microsegmentation required cumbersome agents, hairpinning, or expensive professional services. Zero Networks, instead, found a new paradigm that proves that microsegmentation can be fast, easy, effective, and deployable by anyone to get military-grade security. Reduce the risk of breaches to almost zero with Zero Networks’ MFA-based microsegmentation solution. Request a demo.
Additional Resources For Further Reading On The Topic
To help you stay ahead and deepen your understanding of Zero Trust security, we've curated a list of valuable resources worth exploring.
Relevant Articles and Papers
- Microsoft: Zero Trust Overview
- National Security Agency: Embracing a Zero Trust Security Model
- What is zero trust? A model for more effective security: CSO Online spills the beans on Zero Trust, its principles, and how it boosts security.
- How to segment a network: Lessons learned: Network World shares insights on network segmentation with real-world lessons.
- How do you measure the effectiveness of microsegmentation vs macro segmentation in reducing cyberattacks?
- Zero Trust Architecture (NIST Special Publication 800-207): NIST provides guidelines on building secure systems using ZTA frameworks.
Informative Case Studies
- "BeyondCorp at Google": Google spills the tea on how they successfully implement zero trust architecture across their vast networks.
FAQs in Relation to What is Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity strategy that doesn't trust anyone, not even those already inside the network perimeter. Learn more.
- What are the three foundational concepts of zero trust?
- Continuous verification: Zero trust requires continuous authentication and authorization of users, devices, and network flows based on all available data points, such as user identity, device health, data classification, and anomalies, among others. This means that access requests are scrutinized to determine whether they should be allowed, and access is granted only if the request passes a system of checks.
- Least privileged access: Zero trust assumes that there is no implicit trust granted to assets or user accounts based solely on their physical or network location. Instead, access is granted on a need-to-know basis, and users are granted only the minimum level of access required to perform their job functions. This helps to limit the blast radius of any potential security breaches.
- Risk awareness: Zero trust involves a comprehensive approach to risk management that takes into account the vulnerabilities and threats facing an organization. This requires good visibility into the identities within the organization and what they have access to, including desktops, laptops, other mobile devices, servers, and cloud-based workloads, among other components. By assuming that there is always a risk of breach, zero trust emphasizes the importance of continuous access verification and dynamic policies that are calculated from as many sources of data as possible.
These three foundational concepts are essential for zero trust to work effectively.
- What are the five pillars of Zero Trust?While different sources may have slightly different interpretations of the pillars, the following five are commonly cited:
- Identity Access Management (IAM): This pillar focuses on ensuring that only authorized users have access to resources. It involves verifying the identity of users and devices and granting access based on the principle of least privilege.
- Network Segmentation: This pillar involves dividing the network into smaller segments and controlling access between them. By limiting the scope of each segment, organizations can reduce the impact of a security breach.
- Device and Endpoint Security: This pillar focuses on securing devices and endpoints, such as laptops, smartphones, and IoT devices. It involves ensuring that devices are up-to-date with security patches, using encryption to protect data, and monitoring devices for signs of compromise.
- Application Security: This pillar involves securing applications and APIs, both those developed in-house and those provided by third-party vendors. It involves ensuring that applications are designed with security in mind and that they are tested and monitored for vulnerabilities.
- Data Security: This pillar involves protecting sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII) and intellectual property. It involves identifying critical data assets, classifying data based on its sensitivity, and implementing controls to protect data from unauthorized access.
These pillars are not necessarily sequential, and organizations may need to work on multiple pillars simultaneously to achieve a Zero Trust architecture.
How does Zero Trust Security differ from traditional security models?
- Traditional security models often operate on the premise of a trusted internal network and an untrusted external one. Once a user or device is inside the network, they're generally trusted. Zero Trust Security challenges this by treating every access request as potentially suspicious, regardless of its origin, and demands continuous verification.
Why is Zero Trust Security important in today's digital landscape?
- With the rise of cloud computing, remote work, and sophisticated cyber threats, traditional network perimeters have become blurred. Zero Trust Security addresses this by focusing on users and devices rather than relying solely on network location, providing a more robust defense against potential breaches
Conclusion
After grasping the basics of zero trust security and how it works, it's clear that implementing a true zero trust model is a must for organizations in today's cybersecurity landscape.
Zero Networks is an innovative solution that tackles the challenges of zero trust head-on via our unified zero trust platform that combines microsegmentation, identity segmentation and advanced ZTNA, redefining the game.



